SI derived units with special names
[this page | pdf | references | back links]
There are, according to NIST (2008),
seven base quantities in the International System of Units (SI units), see Introduction to SI units.
Other units are derived from these. However some derived units have special
names and symbols:
|
Quantity
|
Special name
|
Special symbol
|
In terms of other SI units
|
In terms of SI base units
|
|
plane angle
|
radian[1]
|
rad
|
|
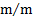
|
|
solid angle
|
steradian[1]
|
sr
|
|
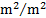
|
|
frequency
|
hertz[2]
|
Hz
|
|
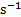
|
|
force
|
newton
|
N
|
|
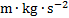
|
|
pressure, stress
|
pascal
|
Pa
|
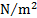
|
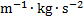
|
|
energy, work, amount of heat
|
joule
|
J
|
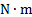
|
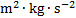
|
|
power, radiant flux
|
watt
|
W
|
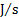
|
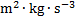
|
|
electric charge, amount of electricity
|
coulomb
|
C
|
|
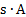
|
|
electric potential difference,
electromotive force, voltage
|
volt
|
V
|
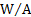
|
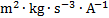
|
|
capacitance
|
farad
|
F
|
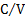
|
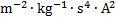
|
|
electric resistance
|
ohm
|
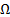
|
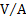
|
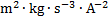
|
|
electric conductance
|
siemens
|
S
|
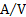
|
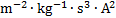
|
|
magnetic flux
|
weber
|
Wb
|
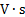
|
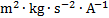
|
|
magnetic flux density
|
tesla
|
T
|
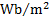
|
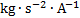
|
|
inductance
|
henry
|
H
|
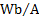
|
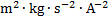
|
|
Celsius temperature
|
degree Celsius[3]
|
°C
|
|
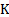
|
|
luminous flux
|
lumen
|
lm
|
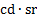
|
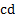
|
|
illuminance
|
lux
|
lx
|
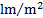
|
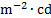
|
|
Activity referred to a radionuclide[4]
|
becquerel
|
Bq
|
|
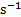
|
|
absorbed dose, specific energy (imparted), kerma
|
gray
|
Gy
|
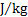
|
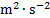
|
|
dose equivalent, ambient dose equivalent, directional dose
equivalent, personal dose equivalent
|
sievert
|
Sv
|
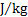
|
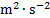
|
|
catalytic activity
|
katal
|
kat
|
|
|
Notes:
[1] The radian and steradian are special names for the
number one that are often used to convey information about the quantity
concerned. In practice (and especially in photometry) the symbols rad and sr
are used where appropriate.
[2] The hertz is normally only used for periodic phenomena.
Likewise the becquerel is normally only used for stochastic phenomena relevant
to the applicable radionuclide.
[3] The degree Celsius is the special name for the kelvin
when used to express Celsius temperatures. The two are equal in size, so a
temperature difference is the same in either scale. By definition, the quantity
in Celsius temperature (°C, symbol 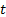 ) is defined by
reference to the quantity in thermodynamic temperature (K, symbol
) is defined by
reference to the quantity in thermodynamic temperature (K, symbol 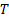 )
by the equation
)
by the equation 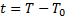 where
where 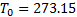 K by
definition.
K by
definition. 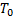 is exactly 0.01
K below the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water
is exactly 0.01
K below the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water
[4] Loosely referred to as the level of radioactivity of the
radionuclide.
NAVIGATION LINKS
Contents | Prev | Next